Senin, 30 Januari 2023
PPPPTK MATEMATIKA | EKSPLORASI TANGRAM
MGMP MATEMATIKA KOTA TANGERANG | CGP BERBAGI
Kamis, 26 Januari 2023
K.H. AHMAD BAHAUDDIN NURSALIM | NGAJI TAFSIR JALALAIN
1. Al Fatihah (Pembuka): 7 Ayat
2. Al Baqarah (Sapi Betina): 286 Ayat
3. Ali Imran (Keluarga Imran): 200 Ayat
4. An Nisa (Wanita): 176 Ayat
5. Al Ma'idah (Jamuan): 120 Ayat
6. Al An'am (Hewan Ternak): 165 Ayat
7. Al-A'raf (Tempat yang Tertinggi): 206 Ayat
8. Al-Anfal (Harta Rampasan Perang): 75 Ayat
9. At-Taubah (Pengampunan): 129 Ayat
10. Yunus (Nabi Yunus): 109 Ayat
11. Hud (Nabi Hud): 123 Ayat
12. Yusuf (Nabi Yusuf): 111 Ayat
13. Ar-Ra'd (Guruh): 43 Ayat
14. Ibrahim (Nabi Ibrahim): 52 Ayat
15. Al-Hijr (Gunung Al Hijr): 99 Ayat
16. An-Nahl (Lebah): 128 Ayat
17. Al-Isra' (Perjalanan Malam): 111 Ayat
18. Al-Kahf (Penghuni-penghuni Gua): 110 Ayat
19. Maryam (Maryam): 98 Ayat
20. Ta Ha (Ta Ha): 135 Ayat
21. Al-Anbiya (Nabi-nabi): 112 Ayat
22. Al-Hajj (Haji): 78 Ayat
23. Al-Mu'minun (Orang-orang mukmin): 118 Ayat
24. An-Nur (Cahaya): 64 Ayat
25. Al-Furqan (Pembeda): 77 Ayat
26. Asy-Syu'ara' (Penyair): 227 Ayat
27. An-Naml (Semut): 93 Ayat
28. Al-Qasas (Kisah-kisah): 88 Ayat
29. Al-'Ankabut (Laba-laba): 69 Ayat
30. Ar-Rum (Bangsa Romawi): 60 Ayat
31. Luqman (Keluarga Luqman): 34 Ayat
32. As-Sajdah (Sajdah): 30 Ayat
33. Al-Ahzab (Golongan-golongan yang Bersekutu): 73 Ayat
34. Saba' (Kaum Saba'): 54 Ayat
35. Fatir (Pencipta): 45 Ayat
36. Ya Sin (Yasin): 83 Ayat
37. As-Saffat (Barisan-barisan): 182 Ayat
38. Sad (Sad): 88 Ayat
39. Az-Zumar (Rombongan): 75 Ayat
40. Ghafir (Yang Mengampuni): 85 Ayat
41. Fussilat (Yang Dijelaskan): 54 Ayat
42. Asy-Syura (Musyawarah): 53 Ayat
43. Az-Zukhruf (Perhiasan): 89 Ayat
44. Ad-Dukhan (Kabut): 59 Ayat
45. Al-Jasiyah (Yang Bertekuk Lutut): 37 Ayat
46. Al-Ahqaf (Bukit-bukit Pasir): 45 Ayat
47. Muhammad (Nabi Muhammad): 38 Ayat
48. Al-Fath (Kemenangan): 29 Ayat
49. Al-Hujurat (Kamar-kamar): 18 Ayat
50. Qaf (Qaf): 45 Ayat
51. Az-Zariyat (Angin yang Menerbangkan): 60 Ayat
52. At-Tur (Bukit): 49 Ayat
53. An-Najm (Bintang): 62 Ayat
54. Al-Qamar (Bulan): 55 Ayat
55. Ar-Rahman (Yang Maha Pemurah): 78 Ayat
56. Al-Waqi'ah (Hari Kiamat): 96 Ayat
57. Al-Hadid (Besi): 29 Ayat
58. Al-Mujadilah (Gugatan): 22 Ayat
59. Al-Hasyr (Pengusiran): 24 Ayat
60. Al-Mumtahanah (Wanita yang Diuji): 13 Ayat
61. As-Saff (Barisan): 14 Ayat
62. Al-Jumu'ah (Hari Jumat): 11 Ayat
63. Al-Munafiqun (Orang-orang yang Munafik): 11 Ayat
64. At-Tagabun (Hari Dinampakkan Kesalahan-kesalahan): 18 Ayat
65. At-Talaq (Talak): 12 Ayat
66. At Tahrim (Pengharaman): 12 Ayat
67. Al-Mulk (Kerajaan): 30 Ayat
68. Al-Qalam (Pena): 52 Ayat
69. Al-Haqqah (Hari Kiamat): 52 Ayat
70. Al-Ma'arij (Tempat Naik): 44 Ayat
71. Nuh (Nabi Nuh): 28 Ayat
72. Al-Jinn (Jin): 28 Ayat
73. Al-Muzzammil (Orang yang Berkelumun): 20 Ayat
74. Al-Muddassir (Orang yang Berselimut): 56 Ayat
75. Al-Qiyamah (Kiamat): 40 Ayat
76. Al-Insan (Manusia): 31 Ayat
77. Al-Mursalat (Malaikat-malaikat yang Diutus): 50 Ayat
78. An-Naba' (Berita Besar): 40 Ayat
79. An-Nazi'at (Yang Mencabut dengan Keras): 46 Ayat
80. 'Abasa (Bermuka Masam): 42 Ayat
81. At-Takwir (Menggulung): 29 Ayat
82. Al-Infitar (Terbelah): 19 Ayat
83. Al-Mutaffifin (Orang-orang yang Curang): 36 Ayat
84. Al-Insyiqaq (Terbelah): 25 Ayat
85. Al-Buruj (Gugusan Bintang): 22 Ayat
86. At-Tariq (Yang Datang di Malam Hari): 17 Ayat
87. Al-A'la (Maha Tinggi): 19 Ayat
88. Al-Gasyiyah (Hari Pembalasan): 26 Ayat
89. Al-Fajr (Fajar): 30 Ayat
90. Al-Balad (Negeri): 20 Ayat
91. Asy-Syams (Matahari): 15 Ayat
92. Al-Lail (Malam): 21 Ayat
93. Ad-Duha (Duha): 11 Ayat
94. Al-Insyirah (Melapangkan): 8 Ayat
95. At-Tin (Buah Tin): 8 Ayat
96. Al-'Alaq (Segumpal Darah): 19 Ayat
97. Al-Qadr (Kemuliaan): 5 Ayat
98. Al-Bayyinah (Pembuktian): 8 Ayat
99. Az-Zalzalah (Kegoncangan): 8 Ayat
100. Al-'Adiyat (Kuda Perang yang Berlari Kencang): 11 Ayat
101. Al-Qari'ah (Hari Kiamat yang Menggetarkan): 11 Ayat
102. At-Takasur (Bermegah-megahan): 8 Ayat
103. Al-'Asr (Masa): 3 Ayat
104. Al-Humazah (Pengumpat): 9 Ayat
105. Al-Fil (Gajah): 5 Ayat
106. Quraisy (Suku Quraisy): 4 Ayat
107. Al-Ma'un (Bantuan): 7 Ayat
108. Al-Kautsar (Nikmat yang Berlimpah): 3 Ayat
109. Al-Kafirun (Orang-orang Kafir): 6 Ayat
110. An-Nasr (Pertolongan): 3 Ayat
111. Al-Lahab (Gejolak Api): 5 Ayat
112. Al-Ikhlas (Ikhlas): 4 Ayat
113. Al-Falaq (Waktu Fajar): 5 Ayat
114. An-Nas (Manusia): 6 Ayat
Kamis, 12 Januari 2023
SPAN PTKIN 2023 | INFORMASI
- PENDAFTARAN SEKOLAH (PDSS) : 17 Januari - 13 Februari 2023
- PENDAFTARAN SISWA : 16 Februari - 04 Maret 2023
- PENGUMUMAN : 03 April 2023
Minggu, 08 Januari 2023
SABRANG MOWO DAMAR PANULUH | SINAU BARENG
Sabtu, 07 Januari 2023
LEARNING PYRAMID
Studies show that varying your study methods and materials will improve your retention and recall of information, and enhance your learning experience. The "learning pyramid", sometimes referred to as the "cone of learning", developed by the National Training Laboratory, suggests that most students only remember about 10% of what they read from textbooks, but retain nearly 90% of what they learn through teaching others. The Learning Pyramid model suggests that some methods of study are more effective than others and that varying study methods will lead to deeper learning and longer-term retention.
A. LECTURE
B. READING
While more effective than Lecture, Reading is still one of the less effective methods for acquiring and retaining information, according to the Learning Pyramid. However, if you are a visual learner, reading textbooks will likely be a more effective learning method for you than for students with non-visual learning styles. Notwithstanding, reading textbooks is a necessary (and required) method of study in most academic settings. There are several strategies for reading textbooks that can greatly improve your ability to retain and recall what you read in your textbook.
C. AUDIO-VISUAL
D. DEMONSTRATION
E. DISCUSSION
F. PRACTICE BY DOING
G. TEACH OTHER
H. CONCLUTIONS
Also, remember that the key here is to vary your method of learning. Don't assume just because the Learning Pyramid suggests that Lectures are the least effective study method for retaining information, that lectures aren't important. Lectures are still very important. Each of the learning methods presented in the Learning Pyramid are important. Even if it's difficult for you to remember everything that is taught during lectures, the notes you take during lecture may be vital to your ability to participate in a discussion of the material later on in your group, or teach the material to others. Vary your study method and focus on the methods and learning styles that yield the best results for you.
SUMBER: https://www.educationcorner.com/the-learning-pyramid.html
Kamis, 29 Desember 2022
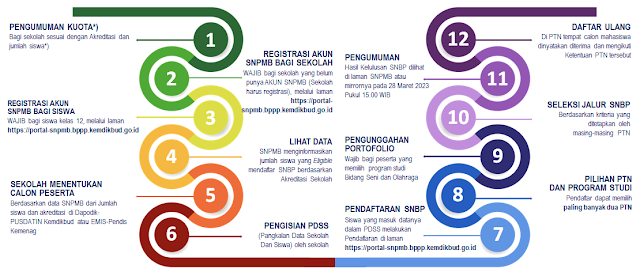
SNPMB 2023 | SNBP
- PDSS merupakan basis data yang berisikan rekam jejak kinerja sekolah dan nilai rapor siswa yang eligible mendaftar.
- PDSS mengakomodasi Kurikulum Nasional 2006 KTSP dan Kurikulum 2013 (Sistem Paket dan SKS). Sekolah yang tidak menggunakan kurikulum nasional tidak diperbolehkan mendaftar PDSS.
- Untuk tahun ajaran dan tingkat yang sama, PDSS mengakomodasi perbedaan kurikulum antara semester ganjil dan genap.
- Pengisian PDSS dilakukan oleh sekolah dan kebenaran data yang diisikan menjadi tanggung jawab Kepala Sekolah.
- SMA/MA/SMK yang mempunyai NPSN.
- Ketentuan Akreditasi:
- Akreditasi A: 40 % terbaik di sekolahnya
- Akreditasi B: 25 % terbaik di sekolahnya
- Akreditasi C dan lainnya: 5% terbaik di sekolahnya
- Mengisi Pangkalan Data Sekolah dan Siswa (PDSS). Data siswa yang diisikan hanya yang eligible sesuai dengan ketentuan.
- Memiliki prestasi akademik dan memenuhi persyaratan yang ditentukan oleh masing-masing PTN
- Memiliki NISN dan terdaftar di PDSS
- Memiliki nilai rapor semester 1 s.d. 5 yang telah diisikan di PDSS
- Peserta yang memilih program studi bidang seni dan olahraga wajib mengunggah Portofolio.
- Setiap siswa dari jurusan IPA, IPS atau Bahasa dizinkan memilih program studi di PTN
- Setiap siswa dapat memilih dua program studi dari satu PTN atau dua PTN
- Jika memilih dua program studi, salah satu harus berada di PTN pada provinsi yang sama dengan SMA/MA/SMK asalnya. Jika memilih satu program studi, dapat memilih PTN yang berada di provinsi mana pun.
- Olahraga;
- Seni Rupa, Desain, dan Kriya;
- Tari (termasuk Sendratasik/Seni Pertunjukan opsi Tari);
- Teater (termasuk Sendratasik/Seni Pertunjukan opsi Teater/Drama);
- Musik (termasuk Sendratasik/Seni Pertunjukan opsi Musik);
- Seni Karawitan;
- Etnomusikologi;
- Fotografi;
- Film dan Televisi;
- Seni Pedalangan.
- Pemeringkatan siswa dilakukan oleh sekolah dengan memperhitungkan nilai rerata semua mata pelajaran semester 1 sampai dengan semester 5.
- Sekolah dapat menambahkan kriteria lain berupa prestasi akademik dalam menentukan peringkat siswa bila ada nilai yang sama.
- Jumlah siswa yang masuk dalam pemeringkatan sesuai dengan ketentuan kuota akreditasi sekolah.